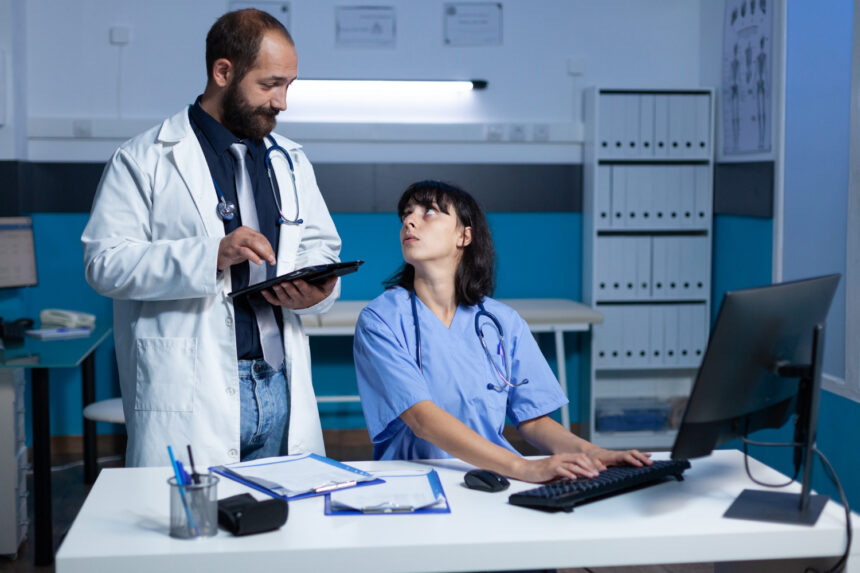
Medical coding services play a crucial role in the healthcare industry by converting patient information into standardized codes. These codes are essential for accurate billing, insurance reimbursement, and maintaining healthcare records. Understanding medical coding is valuable for anyone interested in the mechanics of healthcare billing and the various systems involved.
The demand for skilled medical coders continues to rise as healthcare organizations seek compliance and efficiency. With various coding systems like ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS, coders ensure that healthcare providers receive proper reimbursement for their services. Innovations in medical coding, including outsourcing options and technology-driven solutions, further enhance the effectiveness of these services.
As businesses adapt to changes in healthcare regulations, effective medical coding becomes more important than ever. By recognizing the trends and innovations in this field, healthcare providers can optimize their operations and improve their financial outcomes.
Key Takeaways
- Medical coding is vital for accurate healthcare billing and reimbursement.
- There are different coding systems that coders utilize for various healthcare services.
- Advances in technology and outsourcing shape the future of medical coding services.
Fundamentals of Medical Coding Services
Medical coding services are essential for accurately translating healthcare procedures into standardized codes. This process involves specific industry standards and highlights the critical role these services play in the healthcare system. Understanding these fundamentals is vital for anyone involved in medical billing and coding.
Industry Standards and Classifications
Medical coding uses standardized coding systems to classify medical procedures and diagnoses. The most common coding systems are:
- ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision): Used for coding diagnoses.
- CPT (Current Procedural Terminology): Focuses on medical procedures and services.
- HCPCS (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System): Covers non-physician services, including durable medical equipment.
These standards ensure that healthcare providers can communicate effectively with insurance companies and other entities. Accurate coding leads to proper reimbursement and minimizes claim denials. Regular updates to these coding systems reflect new medical knowledge and practices, making ongoing training essential for coding professionals.
Role and Importance in Healthcare
Medical coding services serve a vital role in the healthcare revenue cycle. They ensure that every service provided is documented, coded, and billed correctly. This process includes:
- Claim Submission: Coders transform patient encounters into coded information for insurance claims.
- Revenue Management: Accurate coding helps healthcare providers maintain positive cash flow and manage resources effectively.
- Compliance: Medical coders help ensure that providers meet regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of audits and penalties.
Without proper coding services, healthcare facilities may struggle with financial stability. Therefore, these services are indispensable for the smooth operation of healthcare management and billing processes.
Types of Medical Coding Systems
Medical coding systems play a crucial role in healthcare. They help healthcare providers, insurers, and patients communicate clearly about medical diagnoses, procedures, and services. The most commonly used coding systems include CPT, ICD, and HCPCS.
Current Procedural Terminology (CPT)
CPT is a coding system developed by the American Medical Association. It is widely used to describe medical, surgical, and diagnostic services.
CPT codes are five-digit numbers. These codes help healthcare providers report their services to insurers for reimbursement. There are three categories of CPT codes:
- Category I: Covers procedures and services.
- Category II: Facilitates performance measurement.
- Category III: Covers emerging technologies and procedures.
Each category serves a specific purpose in billing and documentation, ensuring accuracy in reporting.
International Classification of Diseases (ICD)
ICD is a coding system used to classify diseases and health conditions. The World Health Organization (WHO) maintains this system, which is crucial for tracking health statistics.
ICD codes are alphanumeric. For example, ICD-10-CM codes are used for diagnoses, while ICD-10-PCS codes are used for procedures in hospital settings.
Both ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS serve healthcare providers by detailing patient diagnoses and procedures. This helps in patient care management and supports reimbursement from insurers.
Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS)
HCPCS complements CPT by providing codes for services not included in CPT. This system is crucial for billing Medicare and Medicaid.
HCPCS has two levels of codes.
- Level I: These are CPT codes used for medical services and procedures.
- Level II: These codes address non-physician services, such as ambulance services and durable medical equipment.
Using HCPCS codes ensures a comprehensive billing process for all services and items provided to patients. This system enhances the accuracy and efficiency of medical billing.
Implementation of Medical Coding
Implementing medical coding involves detailed planning and adherence to specific requirements. It is crucial for healthcare providers to understand both hospital operations and specialty needs when applying coding practices.
Hospital and Clinical Applications
In hospitals, medical coding must align with clinical workflows. This ensures accurate patient records and billing. Effective implementation begins with training staff on coding systems and software.
Key components include:
- Staff Training: Coders must be well-versed in the use of coding software and official coding guidelines.
- Documentation Accuracy: Healthcare professionals must provide clear and complete documentation. This reduces errors during the coding process.
- Coding Audits: Regular audits help ensure compliance and accuracy. This can identify gaps in coding practices.
Hospitals often use various coding systems like ICD-10 and CPT to classify diseases and procedures. These systems facilitate effective claims processing and reimbursement.
Specialty-Specific Coding Requirements
Different medical specialties have unique coding needs. Implementation must cater to these requirements to ensure proper coding and billing.
For instance:
- Surgery: Surgical coding requires detailed descriptions of procedures and anatomical sites.
- Pediatrics: Pediatric coding considers growth and developmental milestones.
- Psychiatry: Coding for mental health includes specific codes for diagnoses and treatments.
Understanding these specifications helps in achieving accurate billing and reducing claim denials.
Healthcare providers need to stay updated on changes and guidelines specific to their specialties. Using tools like coding manuals and software supports compliance with these requirements.
Coding Services Management
Effective management of coding services is critical for maintaining quality and efficiency. Proper oversight can help healthcare organizations achieve better accuracy in medical billing and compliance.
Quality Assurance in Coding
Quality assurance ensures that coding practices meet high standards. This includes regular audits, feedback, and ongoing training for coders.
Key practices involve:
- Regular Audits: These checks identify errors and areas for improvement, ensuring coding is accurate and compliant with regulations.
- Continuous Training: Coders should be updated on the latest coding practices and guidelines, enhancing their skill set.
Using quality metrics can track performance and results over time. This focus on quality helps to minimize claim denials and improves overall revenue cycle management.
Outsourcing vs. In-House Coding
Choosing between outsourcing coding services and maintaining an in-house team presents different advantages.
Outsourcing can provide access to a broad pool of experienced coders, which may include:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Many outsourced services offer affordable options due to reduced overhead.
- Expertise: Companies often employ certified coders with specialized knowledge across multiple domains.
In-house coding, on the other hand, allows for:
- Control and Oversight: Organizations can directly manage their coding teams to ensure alignment with internal processes.
- Customization: In-house teams can develop tailored coding practices that fit the specific needs of the healthcare provider.
Each option has unique benefits, and the best choice depends on the organization’s size, needs, and resources.
Trends and Innovations in Medical Coding
The field of medical coding is rapidly evolving due to advancements in technology and changing healthcare practices. These innovations are enhancing the accuracy of coding processes and introducing new ways to improve efficiency.
Impact of Technology on Medical Coding
Technology plays a vital role in transforming medical coding. One major trend is the use of Machine Learning and Natural Language Processing (NLP). These technologies help automate the coding process by analyzing medical documents and improving accuracy.
Computer-Assisted Coding (CAC) is another significant advancement. It leverages AI and human expertise to suggest codes, streamlining the coding workflow. By combining algorithmic suggestions with coder input, CAC increases efficiency.
Additionally, the integration of telehealth is changing billing practices. As telehealth services grow, coding must adapt to include new billing structures and reimbursement models. This shift requires ongoing adjustments and training for coders to keep pace with these changes.
Future of Medical Coding Services
The future of medical coding services holds great promise. The coding market is forecasted to exceed 29 million USD by 2027, indicating growth opportunities in this sector. With this growth comes the need for skilled professionals who can navigate the complexities of coding.
The transition to ICD-11 will also impact coding practices. This new coding system will require additional training for coders to ensure compliance and accuracy.
Finally, there is a focus on value-based care. This approach emphasizes quality over quantity, which means reports will need to reflect patient care outcomes more accurately. Coders will need to be equipped with the right tools and knowledge to meet these evolving demands.